SADA:Semantic adversarial unsupervised domain adaptation for Temporal Action Localization
Abstract
Temporal Action Localization (TAL) is a complex task that poses relevant challenges, particularly when attempting to generalize on new -- unseen -- domains in real-world applications. These scenarios, despite realistic, are often neglected in the literature, exposing these solutions to important performance degradation. In this work, we tackle this issue by introducing, for the first time, an approach for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) in sparse TAL, which we refer to as Semantic Adversarial unsupervised Domain Adaptation (SADA). Our contribution is threefold: (1) we pioneer the development of a domain adaptation model that operates on realistic sparse action detection benchmarks; (2) we tackle the limitations of global-distribution alignment techniques by introducing a novel adversarial loss that is sensitive to local class distributions, ensuring finer-grained adaptation; and (3) we present a novel experimental setup, based on EpicKitchens100, that evaluates multiple types of domain shifts in a comprehensive manner. Our experimental results indicate that SADA improves the adaptation across domains when compared to fully supervised state-of-the-art and alternative UDA methods, attaining a relative performance boost of up to $14\%$.
Overview
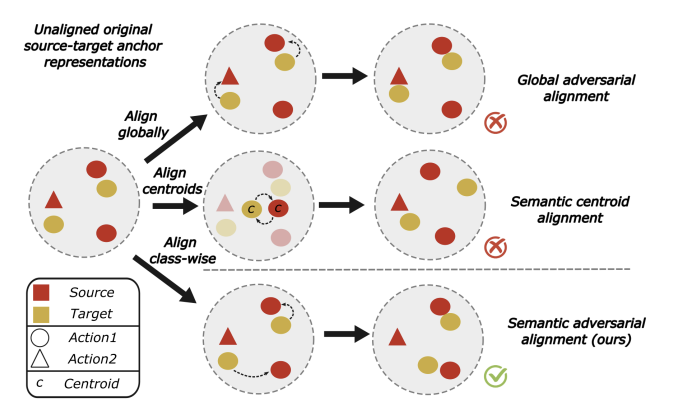
Addressing the problem of feature-misalignment with SADA loss
Our work tackles the inherent challenges in Temporal Action Localization (TAL) within video understanding. TAL involves identifying actions in videos, yet variability in appearance and acquisition creates confusion between similar actions. Traditional supervised methods struggle with unseen data variations, resulting in performance declines. Our approach, Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), aims to bridge this gap by leveraging unlabelled data. However, existing methodologies align domain distributions globally, leading to feature misalignment. Our proposed adversarial loss overcomes this limitation by aligning each action's distribution across both domains, mitigating feature misalignment and enhancing performance.
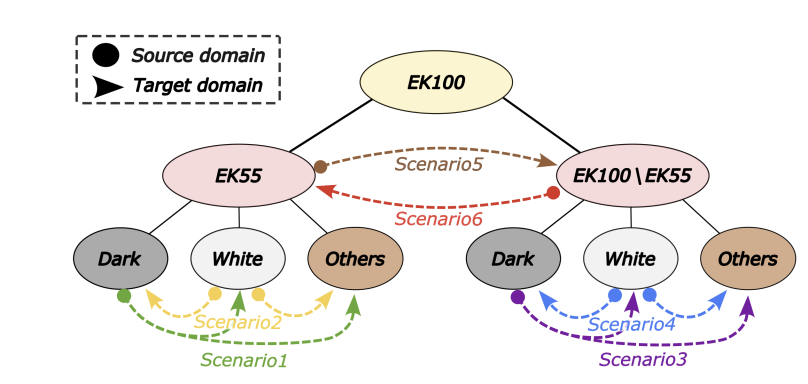
Proposing a new set of benchmarking setups
The current landscape lacks suitable benchmarks to evaluate methodologies in sparse detection for TAL. Existing benchmarks don't cover sparse detection or the simultaneous intersection of labels, crucial aspects in real-world video understanding. To address this inadequacy, we propose a comprehensive suite of 6 new benchmarks based on the EpicKitchens100 dataset. These benchmarks examine appearance and acquisition domain shifts, providing a nuanced evaluation of methodologies in handling real-world scenarios. Our proposed benchmarks aim to fill this gap, enabling a more accurate assessment of models' adaptability to diverse and challenging domains.
Code
The implementation of this project is publicly available here.
BibTeX
Citation entry will be added soon...